Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 O
O determined by aerodynamic levitation
determined by aerodynamic levitationSun, Y.*; Takatani, Tomoya*; Muta, Hiroaki*; Fujieda, Shun*; Kondo, Toshiki; Kikuchi, Shin; Kargl, F.*; Oishi, Yuji*
International Journal of Thermophysics, 45(1), p.11_1 - 11_19, 2024/01
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.07(Thermodynamics)no abstracts in English
Uchibori, Akihiro; Doda, Norihiro; Aoyagi, Mitsuhiro; Sonehara, Masateru; Sogabe, Joji; Okano, Yasushi; Takata, Takashi*; Tanaka, Masaaki; Enuma, Yasuhiro; Wakai, Takashi; et al.
Nuclear Engineering and Design, 413, p.112492_1 - 112492_10, 2023/11
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:72.91(Nuclear Science & Technology)The ARKAIDA has been developed to realize automatic optimization of plant design from safety evaluation for the advanced reactors represented by a sodium-cooled fast reactor. ARKADIA-Design offers functions to support design optimization both in normal operating conditions and design basis events. The multi-level simulation approach by the coupled analysis such as neutronics, core deformation, core thermal hydraulics was developed as one of the main technologies. On the other hand, ARKAIDA-Safety aims for safety evaluation considering severe accidents. As a key technology, the numerical methods for in- and ex-vessel coupled phenomena during severe accidents in sodium-cooled fast reactors were tested through a hypothetical severe accident event. Improvement of the ex-vessel model and development of the AI technology to find best design solution have been started.
Tsuchikawa, Yusuke; Kai, Tetsuya; Abe, Yuta; Oikawa, Kenichi; Parker, J. D.*; Shinohara, Takenao; Sato, Ikken
Journal of Physics; Conference Series, 2605, p.012022_1 - 012022_6, 2023/10
We developed a method to obtain the areal density distribution of boron, which has a large neutron cross section, by means of an energy resolved neutron imaging. Commonly in a measurement of elements with very high neutron sensitivity, the quantitative measurement becomes more difficult with the amount of element due to the neutron self-shielding effect. To avoid this effect, an energy-resolved method using known cross section data was attempted, and a quantitative imaging of such elements was demonstrated at the MLF of J-PARC. This presentation introduces a measurement of melted simulated-fuel assemblies obtained in the research of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant after the severe accident. Energy-dependent neutron transmission rates of the samples were measured by a neutron imaging detector, and were analyzed to obtained the areal density of boron at each position.
 O
O )
) -(SiO
-(SiO )
) measured by aerodynamic levitation
measured by aerodynamic levitationKondo, Toshiki; Toda, Taro*; Takeuchi, Junichi*; Kikuchi, Shin; Kargl, F.*; Muta, Hiroaki*; Oishi, Yuji*
High Temperatures-High Pressures, 52(3-4), p.307 - 321, 2023/06
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.02(Thermodynamics)In order to establish an evaluation method/numerical simulation for nuclear reactor safety under severe accidental conditions, it is necessary to obtain the physical properties, especially fluidity of the relevant molten materials at very high temperatures. In this study, thermophysical properties such as density and viscosity were obtained for (Fe O
O )
) -(SiO
-(SiO )
) , which is a representative composition in the early stage of severe accident. (Fe
, which is a representative composition in the early stage of severe accident. (Fe O
O )
) -(SiO
-(SiO )
) is produced by the contact between the molten oxide of steel, which is the main component of the reactor, and SiO
is produced by the contact between the molten oxide of steel, which is the main component of the reactor, and SiO , which is the main component of concrete. As a result, the physical properties of the (Fe
, which is the main component of concrete. As a result, the physical properties of the (Fe O
O )
) -(SiO
-(SiO )
) mixture were almost the same as those of Fe
mixture were almost the same as those of Fe O
O obtained in previous studies, and it could be concluded that a small amount of SiO
obtained in previous studies, and it could be concluded that a small amount of SiO (about 5 mol.%) did not significantly affect the fluidity of Fe
(about 5 mol.%) did not significantly affect the fluidity of Fe O
O .
.
 and Zr at precisely controlled high temperatures
and Zr at precisely controlled high temperaturesShirasu, Noriko; Sato, Takumi; Suzuki, Akihiro*; Nagae, Yuji; Kurata, Masaki
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 60(6), p.697 - 714, 2023/06
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:72.91(Nuclear Science & Technology)Interaction tests between UO and Zr were performed at precisely controlled high temperatures between 1840 and 2000
and Zr were performed at precisely controlled high temperatures between 1840 and 2000  C to understand the interaction mechanism in detail. A Zr rod was inserted in a UO
C to understand the interaction mechanism in detail. A Zr rod was inserted in a UO crucible and then heat-treated at a fixed temperature in Ar-gas flow for 10 min. After heating in the range of 1890 to 1930
crucible and then heat-treated at a fixed temperature in Ar-gas flow for 10 min. After heating in the range of 1890 to 1930  C, the Zr rod was deformed to a round shape, in which the post-analysis detected the significant diffusion of U into the Zr region and the formation of a dominant
C, the Zr rod was deformed to a round shape, in which the post-analysis detected the significant diffusion of U into the Zr region and the formation of a dominant  -Zr(O) matrix and a small amount of U-Zr-O precipitates. The abrupt progress of liquefaction was observed in the sample heated at around 1940
-Zr(O) matrix and a small amount of U-Zr-O precipitates. The abrupt progress of liquefaction was observed in the sample heated at around 1940  C or higher. The higher oxygen concentration in the
C or higher. The higher oxygen concentration in the  -Zr(O) matrix suppressed the liquefaction progress, due to the variation in the equilibrium state. The U-Zr-O melt formation progressed by the selective dissolution of Zr from the matrix, and the selective diffusion of U could occur via the U-Zr-O melt.
-Zr(O) matrix suppressed the liquefaction progress, due to the variation in the equilibrium state. The U-Zr-O melt formation progressed by the selective dissolution of Zr from the matrix, and the selective diffusion of U could occur via the U-Zr-O melt.
Sato, Ikken; Yoshikawa, Shinji; Yamashita, Takuya; Cibula, M.*; Mizokami, Shinya*
Nuclear Engineering and Design, 404, p.112205_1 - 112205_21, 2023/04
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:90.12(Nuclear Science & Technology)Based on updated knowledge from plant-internal investigations, experiments and model simulations until now, the in-vessel phase of Fukushima-Daiichi Nuclear Power Station Unit 2 was analyzed using the MAAP code. In Unit 2, it is considered that the core material enthalpy was relatively low when it relocated to the lower plenum of the pressure vessel, then, cooled by the coolant and solidified there. Although the MAAP code tended to underestimate the degree of core-material oxidation during the relocation, this probable underestimation was compensated for by an existing study that was considered more reliable, so that more realistic debris conditions in the lower plenum could be obtained. Basic validity of the former prediction of the Unit 2 accident progression behavior was confirmed and detailed boundary condition for the later phase was provided. This boundary condition should be utilized for future studies addressing debris reheating process leading to lower head failure and debris relocation toward the pedestal.
Madokoro, Hiroshi; Yamashita, Takuya; Gaus-Liu, X.*; Cron, T.*; Fluhrer, B.*; Sato, Ikken; Mizokami, Shinya*
Nuclear Technology, 209(2), p.144 - 168, 2023/02
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Nuclear Science & Technology)Takano, Kazuya; Oki, Shigeo; Ozawa, Takayuki; Yamano, Hidemasa; Kubo, Shigenobu; Ogura, Masashi*; Yamada, Yumi*; Koyama, Kazuya*; Kurita, Koichi*; Costes, L.*; et al.
EPJ Nuclear Sciences & Technologies (Internet), 8, p.35_1 - 35_9, 2022/12
The France and Japan teams have carried out collaborative works to have common technical views regarding a sodium-cooled fast reactor concept. Japan has studied the feasibility of an enhanced high burnup low-void effect (CFV) core and fuel using oxide dispersion-strengthened steel cladding in ASTRID 600. Regarding passive shutdown capabilities, Japan team has performed a preliminary numerical analysis for ASTRID 600 using a complementary safety device, called a self-actuated shutdown system (SASS), one of the safety approaches of Japan. The mitigation measures of ASTRID 600 against a severe accident, such as a core catcher, molten corium discharge assembly, and the sodium void reactivity features of the CFV core, are promising to achieve in-vessel retention for both countries. The common design concept based on ASTRID 600 is feasible to demonstrate the SFR core and safety technologies for both countries.
Nakamura, Hironori*; Hayakawa, Satoshi*; Shibata, Akihiro*; Sasa, Kyohei*; Yamano, Hidemasa; Kubo, Shigenobu
Proceedings of 12th Japan-Korea Symposium on Nuclear Thermal Hydraulics and Safety (NTHAS12) (Internet), 7 Pages, 2022/10
In order to evaluate long-term coolablity of the debris-bed with decay heat, a three-dimensional calculation method coupled with the debris bed module was developed in this study. The coupled code calculation results show that natural circulation of the coolant between the hot pool and the cold pool is established through the four intermediate heat exchangers after the activation of the dipped direct heat exchangers. The cold pool with the debris-bed is continually cooled not only by the natural circulation flow, but also by heat transfer to the hot pool through the plenum separation plate between the hot pool and the cold pool. The effect of the three-dimensional flow field around the core catcher on the temperature in the debris-bed is about 20K under the current calculation condition.
 , (FeO
, (FeO )
)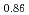 -(ZrO
-(ZrO )
)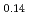 and (FeO
and (FeO )
)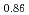 -(UO
-(UO )
)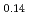
Kondo, Toshiki; Toda, Taro*; Takeuchi, Junichi*; Kargl, F.*; Kikuchi, Shin; Muta, Hiroaki*; Oishi, Yuji*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 59(9), p.1139 - 1148, 2022/09
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:31.61(Nuclear Science & Technology)no abstracts in English
Yamano, Hidemasa; Kubo, Shigenobu; Kan, Taro*; Shibata, Akihiro*; Hourcade, E.*; Dirat, J. F.*
Proceedings of 29th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE 29) (Internet), 10 Pages, 2022/08
In this paper, the approach to event tree development and the scope of the event tree analysis were described with key points on core catcher loading. For the analytical conditions, two core catcher loading conditions were given as bounding and conservative cases. For important heading of the event tree, key important phenomena were included: strong back design, fuel-coolant interaction and quench in the sodium plenum design, jet attack, criticality and coolability on the core catcher. In this paper, preliminary trial quantification was attempted using a probability ranking table which is based on engineering judgement. This event tree analysis has identified the dominant sequence, and clarified the effect of the core catcher loading and effectiveness of design measures. This study suggests that the criticality measure is very important for the core catcher study.
Yamano, Hidemasa; Kubo, Shigenobu; Sasa, Kyohei*; Shibata, Akihiro*; Hourcade, E.*; Dirat, J. F.*
Proceedings of 29th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE 29) (Internet), 9 Pages, 2022/08
This paper describes coolability evaluations of a debris bed with a variety of decay heat removal system (DHRS) operating conditions with a whole vessel model assuming fuel accumulation on the core catcher in a short term. The evaluation tool is a one-dimensional plant dynamics code, Super-COPD, with a debris bed module. The coolability evaluations have indicated that the current core catcher design secures sufficient natural circulation flows around the core catcher to ensure the debris bed cooling when at least one circuit of DHRS was activated. Sensitivity analyses under a pessimistic condition have shown that the debris bed is coolable with at least one circuit of improved DHRS even if most of fuel accumulates on the core catcher in a short term.
Uchibori, Akihiro; Sonehara, Masateru; Aoyagi, Mitsuhiro; Takata, Takashi*; Ohshima, Hiroyuki
Proceedings of International Conference on Fast Reactors and Related Fuel Cycles; Sustainable Clean Energy for the Future (FR22) (Internet), 9 Pages, 2022/04
A new computational code, SPECTRA, has been developed for integrated analysis of in- and ex-vessel phenomena during severe accidents in sodium-cooled fast reactors. The in-vessel thermal hydraulics module includes coupled analytical models for multidimensional multifluid model considering compressibility and relocation of a molten core. A lumped mass model is employed for computing behavior of ex-vessel compressible multicomponent gas including aerosols. This model is coupled with the models for ex-vessel phenomena such as sodium fire. Loss of reactor level event starting from leakage of sodium coolant was computed. Basic capability to evaluate severe accident progress was demonstrated through this analysis.
Uchida, Shunsuke; Karasawa, Hidetoshi; Kino, Chiaki*; Pellegrini, M.*; Naito, Masanori*; Osaka, Masahiko
Nuclear Engineering and Design, 380, p.111256_1 - 111256_19, 2021/08
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:72.21(Nuclear Science & Technology)It is essential to grasp the long-term distributions of FP as well as fuel debris all over the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant (1F) for safe completion of its decommissioning projects. The fuel debris is going to be removed from the plant under the severe conditions of FP being scattered during major decommissioning work, and then, the decommissioning projects are going to be terminated by storing safely the removed debris as recovered fertile materials or as materials for final radioactive disposal. In order to determine the FP distribution in the plant for the long period from the accident occurrence to the termination of the plant decommissioning, procedures for analyzing multi-term FP behaviors were proposed. The proposed procedures should be improved by applying the FP data measured in the plant and validated based on the feedback data. Then, the accuracy-improved procedures should be applied to estimate FP distribution during each period of the decommissioning projects.
Uchida, Shunsuke; Pellegrini, M.*; Naito, Masanori*
Nuclear Engineering and Design, 380, p.111303_1 - 111303_11, 2021/08
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:16.35(Nuclear Science & Technology)Multi-term FP analysis procedures were developed to determine FP distribution all over F1 not only for analyzing accident propagation but also for planning its decommissioning projects. They should be validated based on the measured FP data. One of the useful tools for their validation was application of the dose rate data monitored by the containment atmosphere monitoring system (CAMS). However, in order to compare the data with different characteristics and dimensional units, e.g., FP distribution (kg, Bq) and dose rate (Sv/h), application of the conversion factors bridging them would be effective and useful. In order to prepare speedy, easy-to-handle and tractable procedures to calculate radiation dose rates at the CAMS detector locations, dose rate conversion factors were determined for major source locations and major radionuclides. The dose rates could be easily calculated by multiplying FP amounts obtained with the multiterm FP analysis procedures by the conversion factors.
Okumura, Keisuke
Fission Product Behavior under Severe Accident, p.70 - 72, 2021/05
no abstracts in English
Hidaka, Akihide
Fission Product Behavior under Severe Accident, p.85 - 88, 2021/05
no abstracts in English
Ishigaki, Masahiro; Abe, Satoshi; Shibamoto, Yasuteru; Yonomoto, Taisuke
Nuclear Engineering and Design, 367, p.110790_1 - 110790_15, 2020/10
Times Cited Count:14 Percentile:84.32(Nuclear Science & Technology)no abstracts in English
Hashidate, Ryuta; Kato, Shoichi; Onizawa, Takashi; Wakai, Takashi; Kasahara, Naoto*
Proceedings of ASME 2020 Pressure Vessels and Piping Conference (PVP 2020) (Internet), 9 Pages, 2020/08
Although it is very essential to clarify how the structure collapses under the severe accident conditions, the failure mechanisms in excessive high temperatures are not clarified. However, it is very difficult and expensive to perform structural tests using actual structural materials. Therefore, we propose to use lead alloys instead of actual structural materials. For demonstration of analogy between the failure mechanisms of lead alloys structure at low temperature and those of the actual structures at high temperature, numerical analyses are required. Although the authors proposed inelastic constitutive equations for numerical analyses in 2019, the equations could not successfully express because of large variations observed in the material tests of the lead alloy. In this study, we propose the improved inelastic constitutive equations of the lead alloy on the basis of the material test results used by aged alloy which can stabilized the material characteristic.
Abe, Yuta; Yamashita, Takuya; Sato, Ikken; Nakagiri, Toshio; Ishimi, Akihiro
Journal of Nuclear Engineering and Radiation Science, 6(2), p.021113_1 - 021113_9, 2020/04